Home | Technology | Platform | The Gap in Network Airspace Security & How We Close It
The Gap in Network Airspace Security and How We Close It
Despite all efforts you put in cyber security, your assets remain vulnerable to wireless attacks – you can’t safeguard what you don’t see. This is how Aireye closes this gap and protects your assets

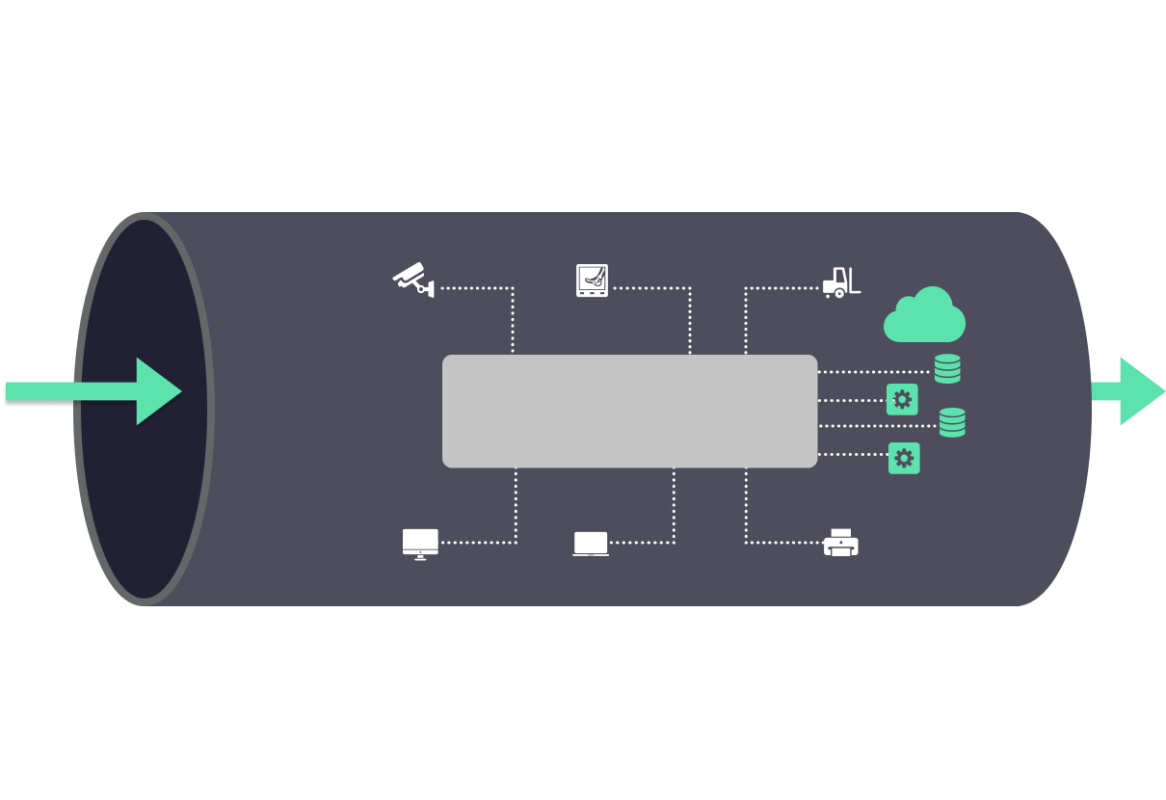
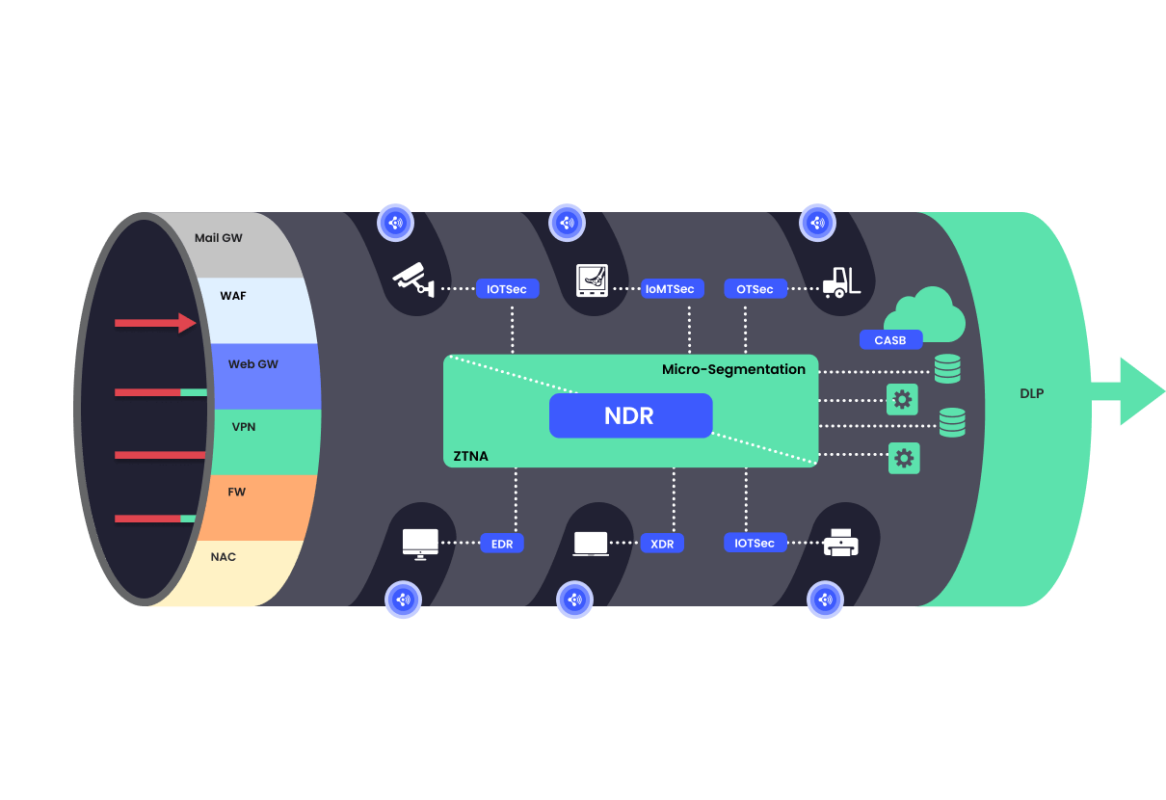
In a world of continuous network attacks
various security solutions are added to the network model.
Let the network be wired, wireless or even virtual such as SASE
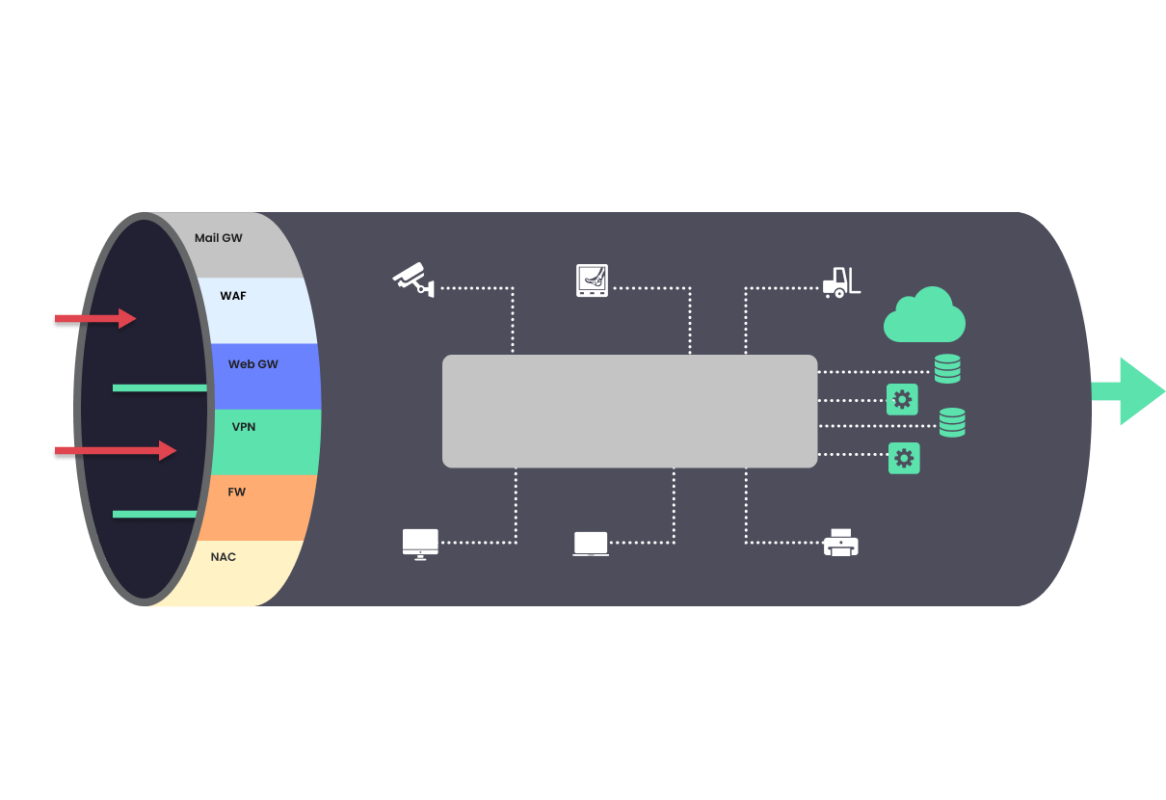
At the entry points
Preventive security solutions are stacked
to enforce that only legitimate traffic enters the network. The purpose of these solutions is to prevent initial compromise of servers and devices on the network and prevent traffic from unknown sources to reach corporate devices.
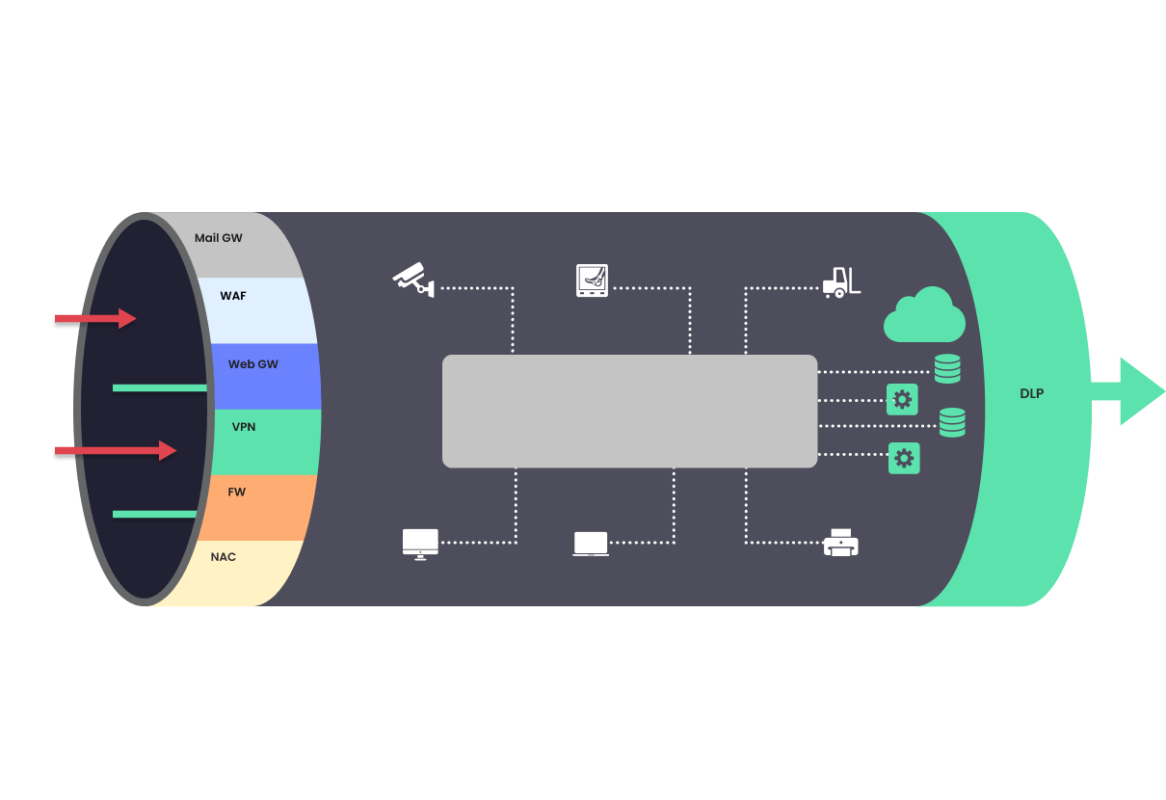
At the exit points
DLP solutions are placed
to ensure that only policy-allowed data leaves the corporate.
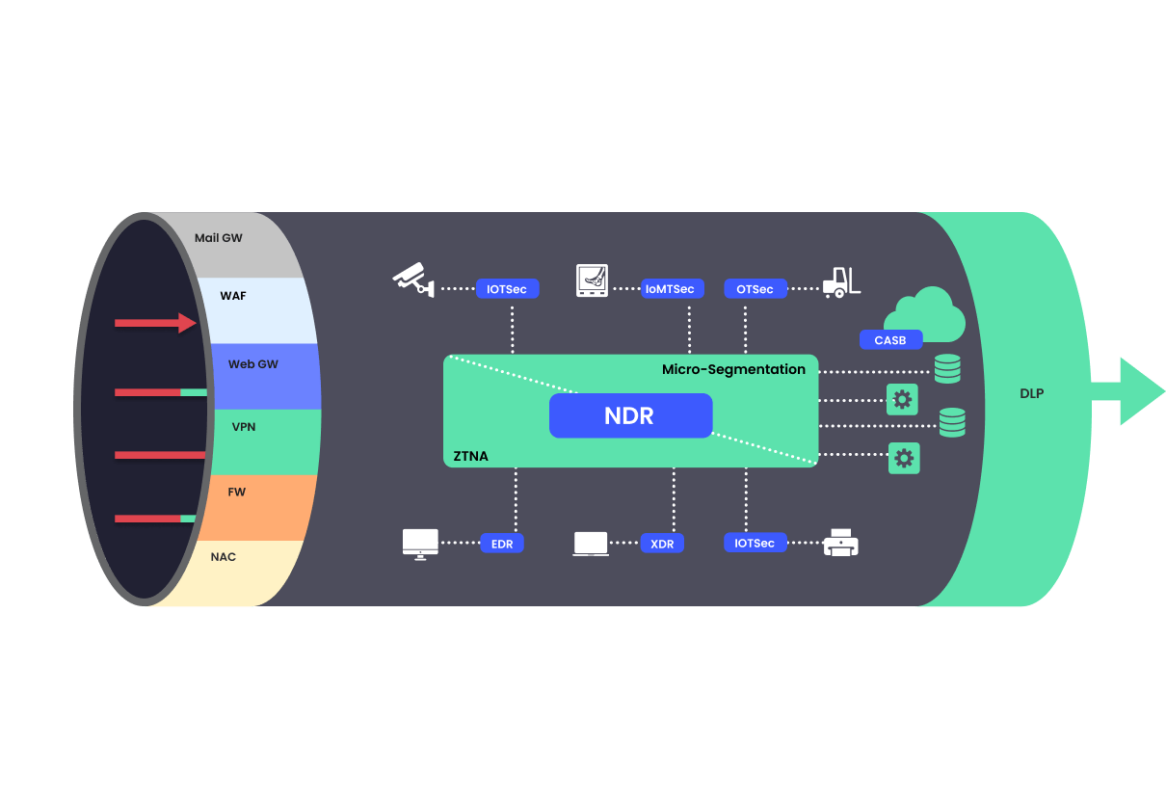
While the above solutions
serve as an initial gatekeeper
additional security solutions are deployed for when an attacker has already established a foothold within the organization.
The wireless capabilities
of the devices on the network
changes the above illustration
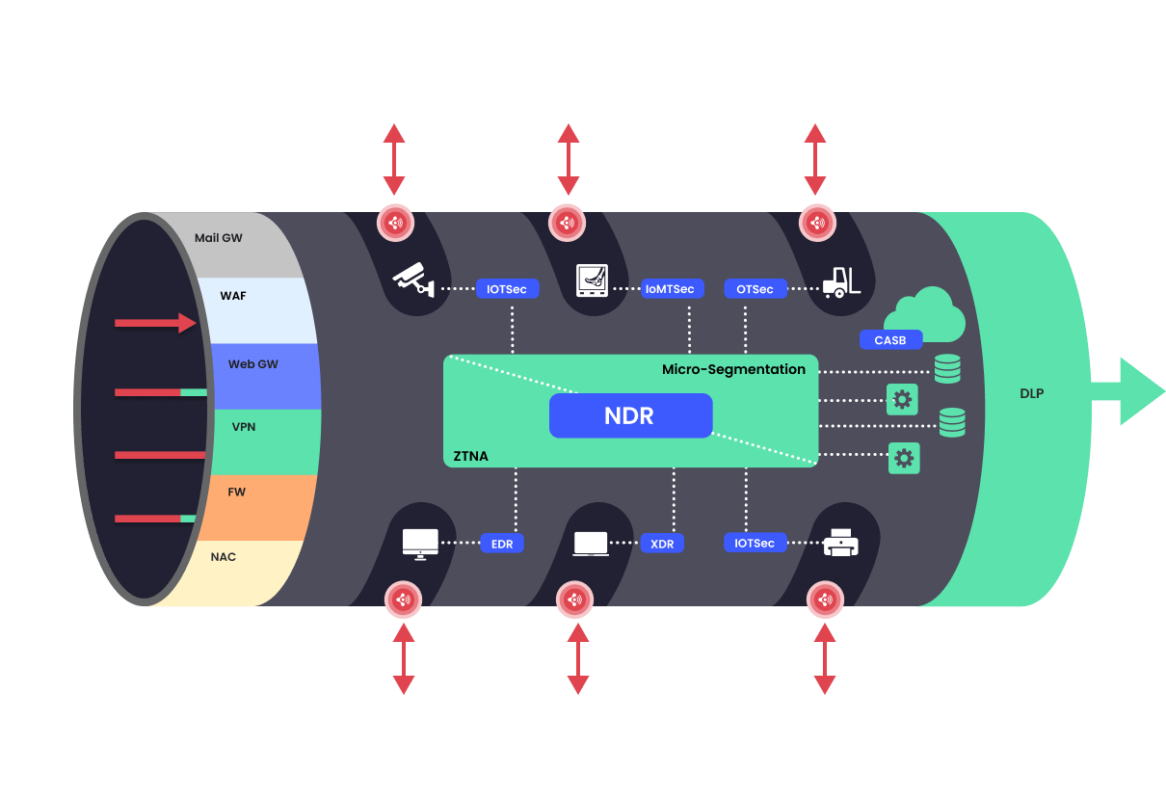
These open up a new attack surface
uncovered by existing security solutions.
While wireless capable devices are connected securely to the corporate network (whether wired or wireless), they are inherently open to accepting and processing network traffic transmitted by any other device in their proximity.
They are also capable of sending out insecure network traffic.
![]() In essence, today’s corporate network is perforated with gaps generated by these corporate-owned dual-connected devices, aka Wireless Receptors.
In essence, today’s corporate network is perforated with gaps generated by these corporate-owned dual-connected devices, aka Wireless Receptors.
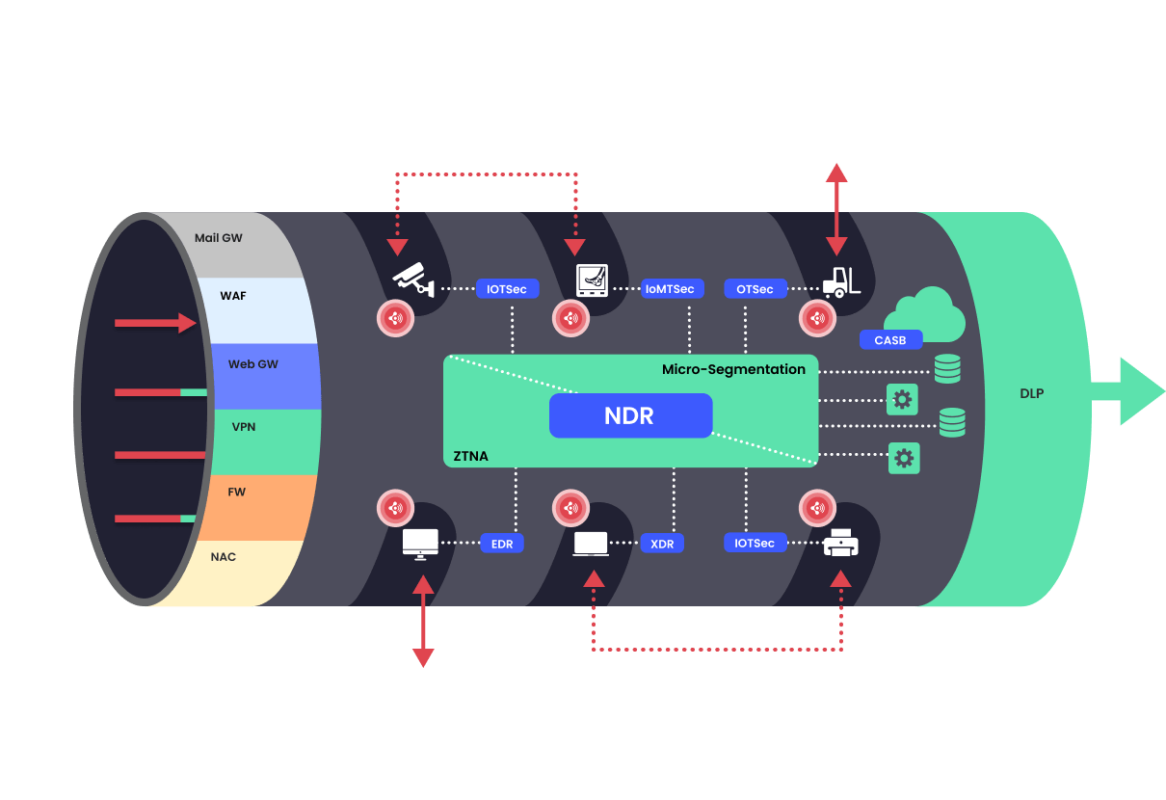
Wireless Receptors
also create internal insecure network paths.
These internal networks, called Shadow Networks, additionally defeat micro-segmentation solutions.
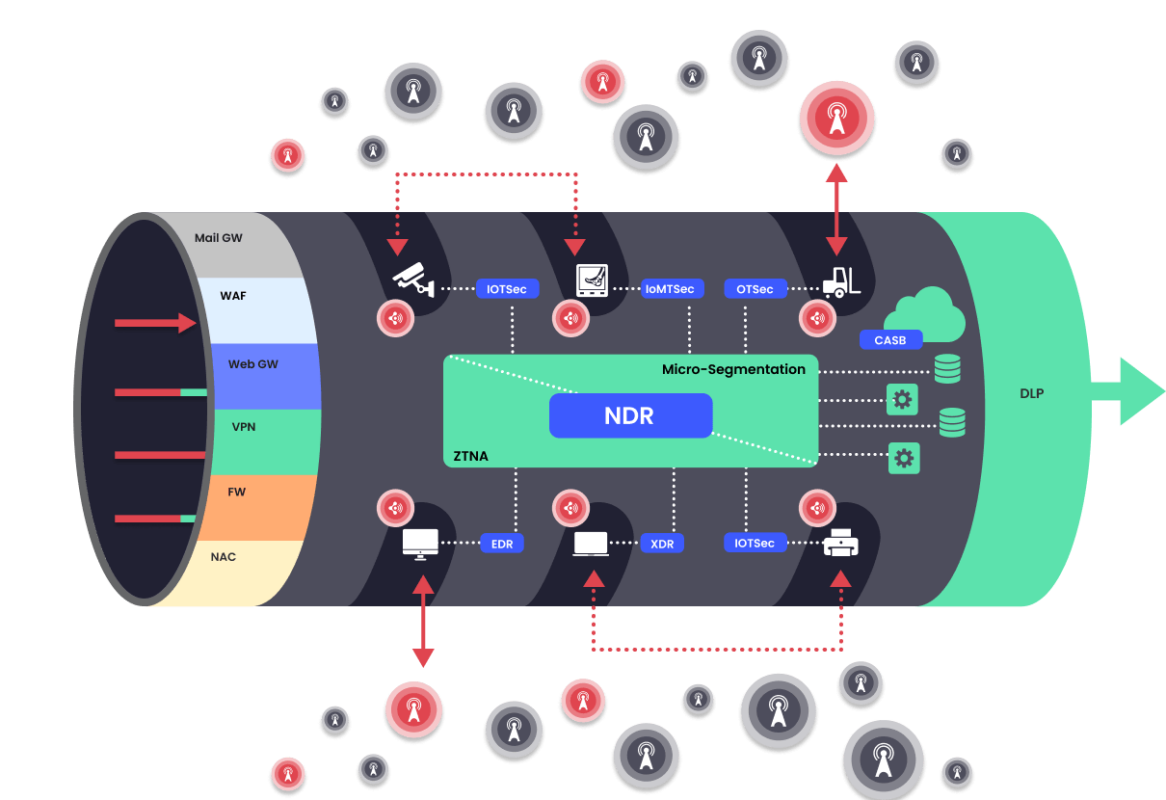
The corporate network
is surrounded by an infinite number of Antenna for Hire.
These are wireless devices that broadcast in the corporate network. These can be laptops, open-source Access Points (openWRT), the wireless router in a neighboring cafe, personal mobile phones, OT and IoT devices such as Wifi cameras, TVs, monitors, A/C units, etc.
![]() Today’s attack tools can compromise an Antenna for Hire remotely and through software-based tools. From there the attacker can connect wirelessly to the Wireless Receptor and penetrate the network or act as an exfiltration destination.
Today’s attack tools can compromise an Antenna for Hire remotely and through software-based tools. From there the attacker can connect wirelessly to the Wireless Receptor and penetrate the network or act as an exfiltration destination.
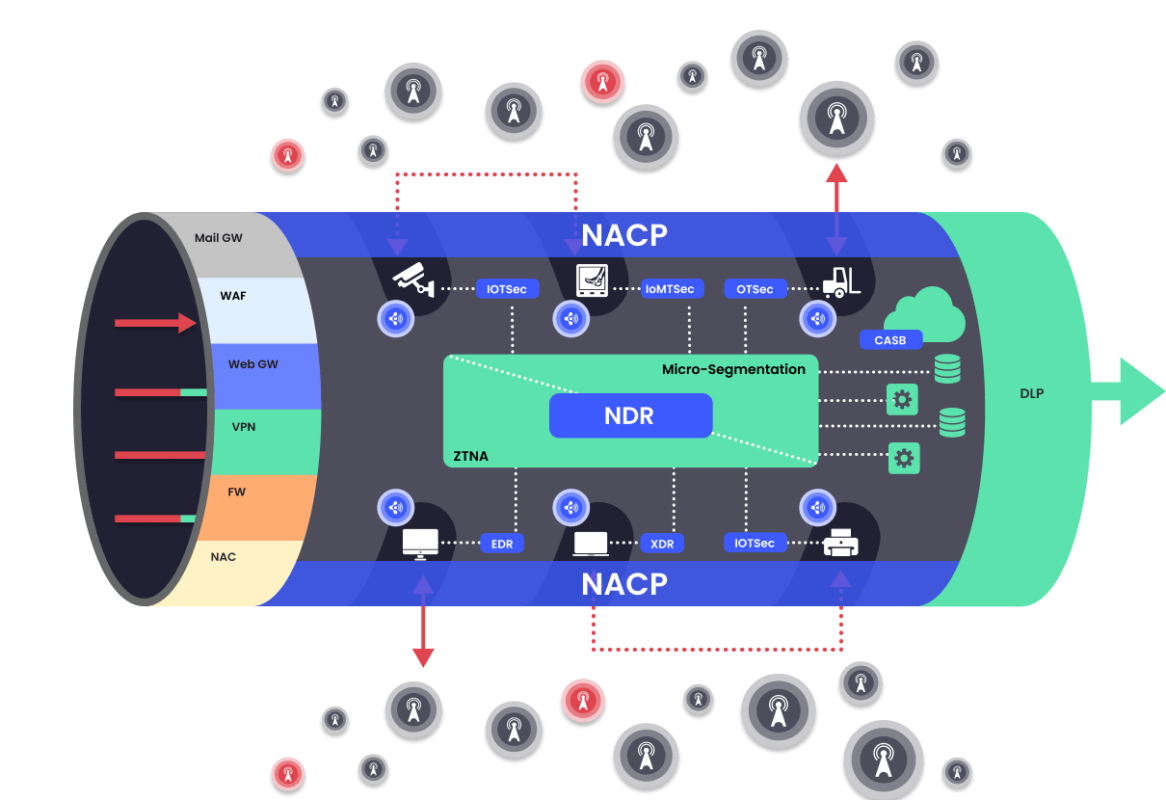
Network Airspace Control and Protection (NACP)
is an additional network security layer
that closes these wireless holes. The NACP prevents the over-the-air attack from entering and exiting the corporate network as well as extends network and micro segmentation by preventing over- the-air lateral movement.
